EBR Systems has announced the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) for its WiSE (Wireless Stimulation Endocardially) technology for cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). This IDE enables EBR Systems to start a major US study—SOLVE CRT—to establish safety and effectiveness in support of US approval.
“WiSE is a unique, significant technology that is cleared for use in Europe and has proven very beneficial thus far,” says Jagmeet Singh, principal investigator for the planned study, and associate chief of Cardiology and professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, USA. “This important medical advance addresses major shortcomings in current CRT implants and could dramatically improve success rates for heart failure patients around the globe.”
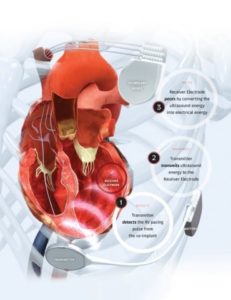
WiSE is the world’s only wireless, endocardial pacing system for stimulating the heart’s left ventricle. This has long been a goal of cardiac pacing companies since internal stimulation of the left ventricle is recognised as a potentially superior, more anatomically correct pacing location.
The technology consists of a tiny electrode implanted in the left ventricle. With every heartbeat, it receives a synchronised ultrasound signal from a small transmitter placed between two ribs. Those sound waves are converted to electrical energy, providing cardiac pacing.
Studies have demonstrated that successful CRT therapy reduces heart failure symptoms, hospitalisations and mortality by synchronising the left and right ventricles. However, approximately 30% of patients receiving conventional CRT do not respond to the therapy. A major cause of this shortcoming is believed to be the inconsistency of results achieved using wire leads to transmit pacing pulses to the left ventricle’s epicardial surface.
Although it is generally accepted that internal stimulation of the left ventricle is preferable, wire leads or large implants placed inside the left ventricle can cause clots, heart attacks or stroke. Consequently, this pacing location is not currently used by commercially-available CRT systems in the United States.
EBR Systems claims that its WiSE technology could potentially benefit 1.5 million patients worldwide.
Results of the SELECT-LV study were presented in May 2016 by professor of Medicine, Vivek Reddy (Mt Sinai Hospital, New York, USA) at the Heart Rhythm Society Scientific Sessions in San Francisco. In a study of 35 patients who had failed conventional CRT therapy, 97% were implanted successfully with WiSE technology. Of the thirty-three patients who reached the six-month effectiveness endpoint, 85% improved their clinical composite score which is a measure of symptom improvement.
“Patients who have failed conventional CRT continue to deteriorate from their heart failure and are repeatedly subjected to costly hospitalisations,” says Ohio State University professor of Medicine, William Abraham, heart failure expert and director of OSU’s Wexner Medical Center and member of the study’s steering committee. “We have actively sought new treatment alternatives for this large and growing patient population.”
He continues, “WiSE is easily the most promising solution to this costly problem. Its tiny receiver makes endocardial, left ventricular pacing possible for the first time. There is nothing like it in cardiology.”
About SOLVE-CRT
SOLVE-CRT (Stimulation of the left ventricle endocardially–CRT) will be a prospective, randomised controlled trial aimed to enrol 350 patients who have either failed conventional CRT or who were previously untreatable with conventional CRT systems.
The SOLVE-CRT study will be using generally-accepted measures of safety and efficacy as primary endpoints at six months. EBR Systems anticipates starting this clinical trial in mid-2017.
The company also plans to introduce its second-generation WiSE technology in Europe in early 2017 and subsequently include it in the SOLVE-CRT study. The transmitter size has been reduced by half, making it smaller than a conventional pacemaker. Second generation battery life is expected to equal conventional CRT systems.
WiSE is CE mark approved in Europe. In June 2105 it was selected Favorite Innovation winner at the annual EHRA EUROPACE-CARDIOSTIM congress in Milan, Italy.











