 Biosense Webster has announced the launch of the latest version of the its three-dimensional (3D) heart mapping system used in cardiac ablation procedures—Carto 3 system version 8.
Biosense Webster has announced the launch of the latest version of the its three-dimensional (3D) heart mapping system used in cardiac ablation procedures—Carto 3 system version 8.
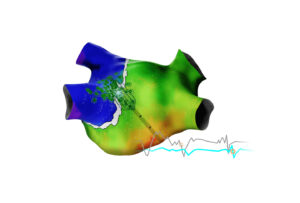
The software features new modules including the Carto Elevate module and Cartosound Fam module, designed for efficiency, reproducibility, and accuracy for electrophysiologists performing catheter ablation procedures to treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and other arrhythmias.
“We are pleased to announce this new version of our Carto 3 system, which reflects our continued focus on harnessing the latest science and technology to advance tools for electrophysiologists to treat cardiac arrhythmias,” said Jasmina Brooks, president, Biosense Webster. “The Carto 3 system has been the cornerstone of catheter ablation procedures for more than a decade, helping electrophysiologists make treatment decisions. This new version advances the Carto 3 mapping and ablation experience through enhanced signal analysis, improved substrate characterisation, and utilisation of ultrasound technology.”
“Carto 3 system version 8 incorporates a novel component, the Cartosound Fam module, which, for the first time, utilises artificial intelligence (AI) to reconstruct the left atrial anatomy, streamlining the process for electrophysiologists,” said Luigi Di Biase, (Montefiore-Einstein Health System, New York, USA). “By eliminating the need for manual contouring, the new system represents a new approach to anatomy creation, improving the efficiency of the procedure workflow.”
“Accuracy and precision in mapping the heart when treating cardiac arrhythmias are critical for electrophysiologists, and therefore, our patients,” continued Di Biase. “The Carto Elevate module raises the bar for electro-anatomical mapping systems used in catheter ablation procedures. Capabilities such as multipolar mapping make a difference for electrophysiologists in the electrophysiology lab, facilitating a reduction in far-field signal and increased focus on the electrical signals in the patient’s heart that contribute to arrhythmias.”












